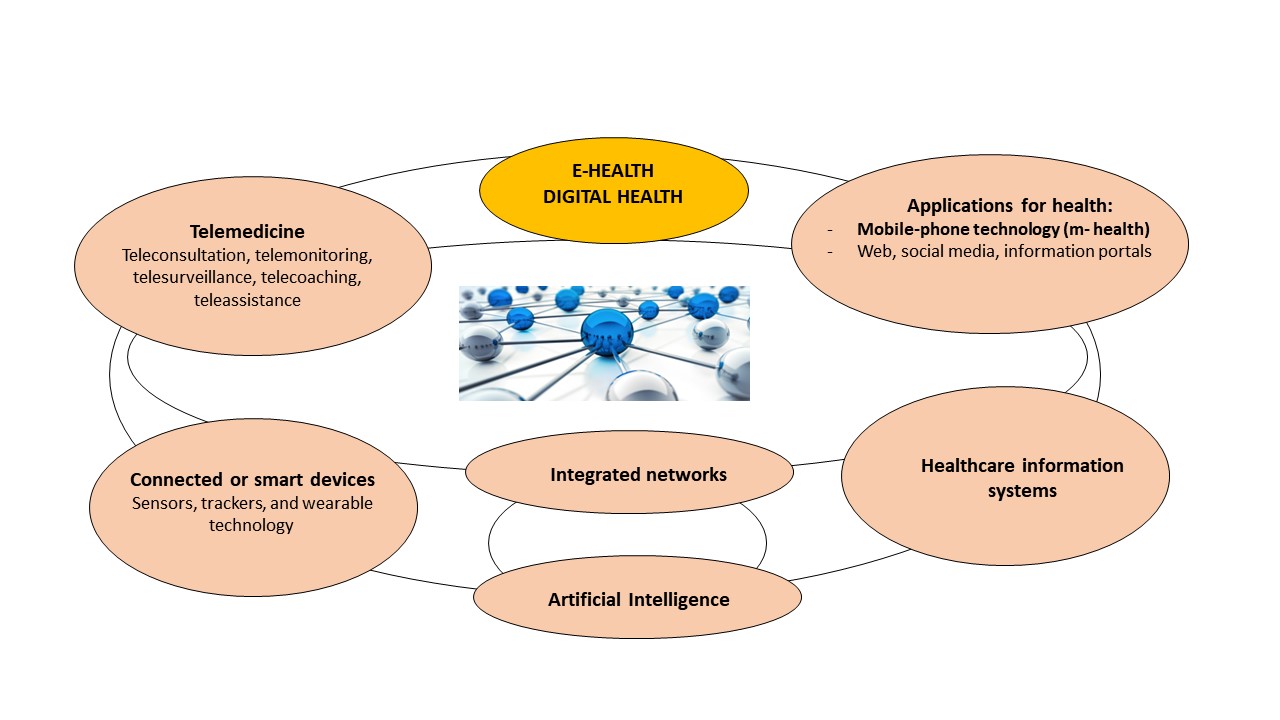
E-health, also known as “digital health”, corresponds to the use of information technology applied to the field of health. It is an extremely broad domain, which regroups the main following areas:
- Telemedicine: It corresponds to the use of digital communication technologies to provide healthcare remotely. Telemedicine covers various applications, such as teleconsultation (medical visit with a practitioner at a distance), telemonitoring (recording and monitoring of parameters at a distance), telecoaching and tele-rehabilitation (with for example physical activity programs followed at a distance by patients) or even telemonitoring (allowing remote monitoring of patients and rapid intervention in the event of a signal). Telemedicine thus provides access to remote medical services, which can be made available at the patient’s home as well as in private or public institutions.
- Applications dedicated to education and information of patients about their health: many applications are currently available through web, social networks, applications on mobile phones, which can be grouped under the term “m-health” or “mobile-health technology”.
- Health information systems: These include all the informatic systems and communication methods used to manage medical information and health data within health institutions and establishments.
- Connected or smart devices: These include sensors, trackers, smart medical devices, some of which can be worn directly by the person (this is known as “wearable technology”).
These digital health applications can use techniques derived from Artificial Intelligence or integrated networks to develop them or improve their functioning.
For more information on telemedicine and digital health applications in vascular diseases, you can consult the following articles:
